Amorphization driven Na-alloying in SixGe1−x alloy nanowires for Na-ion batteries†
Abstract
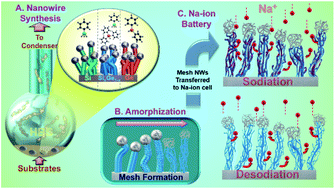
Here we report the use of 1D SixGe1−x (x = 0.25, 0.5, 0.75) alloy nanowires (NWs) as anode materials for Na-ion batteries (NIBs). The strategy involves the synthesis of crystalline SixGe1−x NWs via the solution–liquid–solid (SLS) mechanism, followed by amorphization to activate the material for Na-ion cycling within a NIB. This study demonstrates the successful activation of SixGe1−x amorphous NW alloys, with a-Si0.5Ge0.5 delivering 250 mA h g−1 as compared to a-Ge NWs delivering only 107 mA h g−1 after 100 cycles. Also, amorphization proved to be a critical step, since crystalline NWs failed to activate in NIBs. However, Si NWs performed poorly during Na-ion cycling even after amorphization, and this behavior was explained by poor comparative Na-ion diffusivity. Further investigations on the impact of the relative content of Ge within the amorphized SixGe1−x NWs, Na-ion diffusivity and electrode degradation during cycling were also performed. Notably, the incorporation of Ge in the a-SixGe1−x alloy boosted Na ion diffusivity in the amorphized alloy, resulting in improved cycling performance and rate capability as compared to parent a-Si and a-Ge NWs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...