Lipid-mimicking phosphorus-based glycosidase inactivators as pharmacological chaperones for the treatment of Gaucher's disease†
Abstract
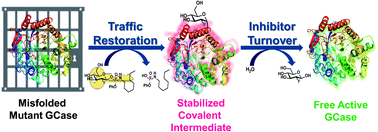
Gaucher's disease, the most prevalent lysosomal storage disorder, is caused by missense mutation of the GBA gene, ultimately resulting in deficient GCase activity, hence the excessive build-up of cellular glucosylceramide. Among different therapeutic strategies, pharmacological chaperoning of mutant GCase represents an attractive approach that relies on small organic molecules acting as protein stabilizers. Herein, we expand upon a new class of transient GCase inactivators based on a reactive 2-deoxy-2-fluoro-β-D-glucoside tethered to an array of lipid-mimicking phosphorus-based aglycones, which not only improve the selectivity and inactivation efficiency, but also the stability of these compounds in aqueous media. This hypothesis was further validated with kinetic and cellular studies confirming restoration of catalytic activity in Gaucher cells after treatment with these pharmacological chaperones.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...