Design, synthesis and in silico screening of benzoxazole–thiazolidinone hybrids as potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 proteases†
Abstract
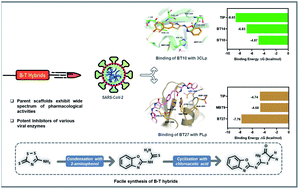
Hybrid molecules in the recent years have gained significant importance in drug research as promising therapeutic agents. We report a novel combination of two such bioactive scaffolds (benzoxazole and 4-thiazolidinone B–T hybrids) as inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2. The study uses an in silico approach to identify the potential of B–T hybrids as possible inhibitors of the SARS-CoV-2 proteases. Molecular docking was employed to identify the interactions of B–T hybrids with the two proteases – 3CLp (the 3-chymotrypsin-like protease) and PLp (the papain-like protease). Docking results of the screened 81 hybrids indicated that BT10 and BT14 interacted with the catalytic dyad residue of 3CLp (Cys145) with the best binding energy. MD simulations revealed that BT10 formed stable interactions via 4 hydrogen bonds with the catalytic site residues of 3CLp. In the case of PLp, BT27 and MBT9 interacted with the catalytic triad residue of PLp (His272) with high binding energy. MD simulations demonstrated that the reference drug Tipranavir relocated to the thumb region of the protease whereas BT27 remained in the active site of PLp stabilized by 2 hydrogen bonds, while MBT9 relocated to the BL2 loop of the palm region. The MM-PBSA and interaction entropy (IE) analysis indicated that BT14 exhibited the best ΔG (of −6.83 kcal mol−1) with 3CLp, while BT27 exhibited the best ΔG (of −7.76 kcal mol−1) with PLp. A four-step synthetic procedure was employed to synthesize the B–T hybrids starting from ammonium thiocyanate. The short-listed compounds in the case of 3CLp were synthesized and characterized using IR, NMR, and HRMS spectroscopic techniques.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...