Understanding the effects of nucleophiles in fast living cationic polymerisation of isobutyl vinyl ether in a microflow system from stability and activity of propagating chains
Abstract
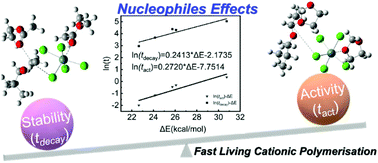
Previous studies on fast living cationic polymerisation have rarely focused on the effects of nucleophiles, which are crucial in determining a suitable initiation system. In this work, taking the polymerisation of isobutyl vinyl ether (IBVE) as an example, the effects of various nucleophiles, namely ethyl acetate, 1,4-dioxane, 1,3-dioxolane, diethyl ether, and ethyl propionate, on the activity and stability of the propagating chains were systematically examined in a microflow system, in which IBVE-HCl/SnCl4 was selected as the initiation system and 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate was employed as an effective end-capping agent for 1H NMR spectroscopy measurements. The characteristic time of activity (tact) and the half-life of stability (tdecay) exhibited almost linear proportional relationships, revealing that the nucleophiles did not alter the relative values of activity and stability, acting simply to improve the controllability of the cationic polymerisation process. Furthermore, a density functional theory simulation method was established to calculate the dissociation energy of IBVE/SnCl4/Nus (ΔE). Approximately linear relationships between ln(tact) or ln(tdecay) and ΔE were found, indicating the potential of theoretical calculations to estimate the activities and stabilities of the propagating chains in this process.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...