Reactivity of a carbonyl moiety in organotin(iv) compounds: novel Pd(ii) and Cu(ii) complexes supported by organotin(iv) ligands†
Abstract
Hydrolysis of [2-{(CH2O)2CH}C6H4]SnPh3 (1) results in the isolation of [2-(O![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH)C6H4]SnPh3 (2) in a very good yield. Reduction of 2 with NaBH4 gives an almost quantitative yield of [2-(HOCH2)C6H4]SnPh3 (3), when 2 is treated with appropriate amines in the absence of any solvent, [2-(4′-PyCH2N
CH)C6H4]SnPh3 (2) in a very good yield. Reduction of 2 with NaBH4 gives an almost quantitative yield of [2-(HOCH2)C6H4]SnPh3 (3), when 2 is treated with appropriate amines in the absence of any solvent, [2-(4′-PyCH2N![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH)C6H4]SnPh3 (4) and [2-{3′,5′-(MeOOC)2–C6H3N
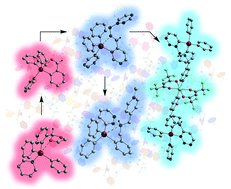
CH)C6H4]SnPh3 (4) and [2-{3′,5′-(MeOOC)2–C6H3N![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH}C6H4]SnPh3 (5) are isolated in high yields. Adding NaBH4 to a THF solution of 4 leads to [2-(4′-PyCH2NH–CH2)C6H4]SnPh3·BH3 (6), the first aryltin(IV) compound with a ligand containing a secondary amine functional group coordinated to the metal centre. The reaction of 4 with [PdCl2(NCMe)2] and [Cu(hfac)2·(H2O)] (hfac = hexafluoroacetylacetonate) in a 2 : 1 molar ratio gave the corresponding heterometallic complexes [{2-(4′-PyCH2N
CH}C6H4]SnPh3 (5) are isolated in high yields. Adding NaBH4 to a THF solution of 4 leads to [2-(4′-PyCH2NH–CH2)C6H4]SnPh3·BH3 (6), the first aryltin(IV) compound with a ligand containing a secondary amine functional group coordinated to the metal centre. The reaction of 4 with [PdCl2(NCMe)2] and [Cu(hfac)2·(H2O)] (hfac = hexafluoroacetylacetonate) in a 2 : 1 molar ratio gave the corresponding heterometallic complexes [{2-(4′-PyCH2N![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2)C6H4SnPh3}2PdCl2] (7) and [{2-(4′-PyCH2N
CH2)C6H4SnPh3}2PdCl2] (7) and [{2-(4′-PyCH2N![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2)C6H4SnPh3}2Cu(hfac)2] (8), respectively. The purity of the compounds was confirmed by elemental analysis and high-resolution mass spectrometry. Multinuclear NMR spectroscopy was used to investigate the solution behaviour of these compounds and the molecular structures for 1, 2, and 4–8 were established by single-crystal X-ray diffraction.
CH2)C6H4SnPh3}2Cu(hfac)2] (8), respectively. The purity of the compounds was confirmed by elemental analysis and high-resolution mass spectrometry. Multinuclear NMR spectroscopy was used to investigate the solution behaviour of these compounds and the molecular structures for 1, 2, and 4–8 were established by single-crystal X-ray diffraction.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...