V-shaped fluorophores with a 1-methyl-4,5-bis(arylethynyl)imidazole skeleton displaying solid-state fluorescence, acid responsiveness, and remarkable fluorescence solvatochromism†
Abstract
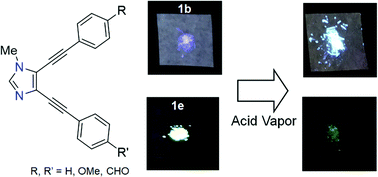
Novel V-shaped fluorophores with an imidazole skeleton composed of arylethynyl moieties were developed. Their HOMO–LUMO energy gaps were well controlled by the introduction of electron-withdrawing or -donating groups in the aryl moiety. Compounds with different substituents at the 4- and 5-positions were selectively synthesized exploiting the difference in reactivity between the iodo and bromo groups. All compounds synthesized displayed fluorescence not only in solution but also in the solid state. The compound with a donor–acceptor structure displayed a fluorescence maximum with a wavelength over 500 nm and a large Stokes shift of about 150 nm, due to its intramolecular charge transfer character. In the solid state, the synthesized compounds have planar structures, indicating an expansion of π-conjugation. Upon exposure of the compounds in the solid state to acid vapor, the fluorescence of the compounds with acceptor groups was quenched, and that of the others shifted to longer wavelengths.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...