Amphiphilic RGD and GHK peptides synergistically enhance liposomal delivery into cancer and endothelial cells†
Abstract
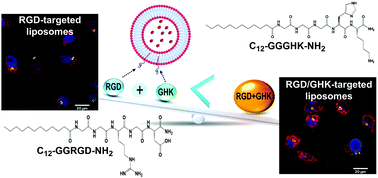
This study reveals enhanced cancer-targeting properties of a peptide composition consisting of RGD and GHK, recognized as an important cell adhesion factor and pleiotropic modulator of cellular functions, respectively. C12-GGRGD-NH2 and C12-GGGHK-NH2 amphiphilic peptides comprising a lauric acid moiety capable of insertion into the liposomal membrane were synthesized. Composite liposomes made of phosphatidylcholine, cationic DOTAP and the peptide(s) were used at a pre-optimized PC : DOTAP ratio of 35 : 1 and relative peptide content of 4 mol%. The RGD/GHK dual targeting system exhibited a profound synergistic effect on the cellular uptake of the liposomal formulation in integrin-overexpressing cancer and endothelial cells. Effective liposome activation via in situ association of the amphiphilc peptide(s) with the liposomal membrane was carried out. Dual peptide-modified liposomes loaded with doxorubicin or paclitaxel induced enhanced cytotoxicity accompanied by oxidative stress and mitochondria depolarization in the target cells. The study shows joint potential of RGD and GHK tripeptides as a targeting system in anticancer/antiangiogenic therapy and provides a methodology for screening of combinatorial effects of bioactive peptides displayed on the liposome surface. Peptide-modified liposomes were employed to reveal GHK–heparin binding, suggesting a potential complementary role of glycosaminoglycans in RGD/GHK-mediated liposomal delivery.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...