Efficient bioconversion of high-concentration d-fructose into d-mannose by a novel N-acyl-d-glucosamine 2-epimerase from Thermobifida halotolerans
Abstract
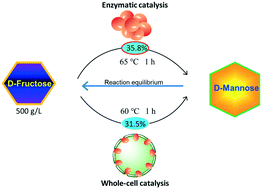
The synthesis of mannose is of great value because it is the only glyconutrient used for clinical applications. Here, we performed the enzymatic bioconversion of D-fructose to D-mannose using a recombinant thermostable N-acyl-D-glucosamine 2-epimerase (ThMI) from a Thermobifida halotolerans engineered strain. The enzymatic bioconversion produced 180 g L−1D-mannose from high-concentration D-fructose (500 g L−1) in 1 h by recombinant ThMI, resulting in a maximum bioconversion ratio of 35.8%. The recombinant resting cells at a density of 10 OD600 produced 157 g L−1D-mannose from 500 g L−1D-fructose in 1 h. These results suggest that the novel biocatalyst system developed in this study can be applied for large-scale industrial production of D-mannose.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Biocatalysis: A cross-journal collection


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...