Reaction mechanism and dynamics for C8-hydroxylation of 9-methylguanine radical cation by water molecules†
Abstract
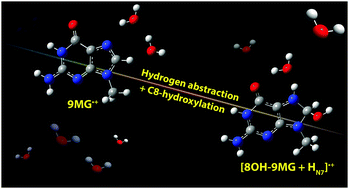
In contrast to their spontaneous deprotonation in aqueous solution, reactions of guanine and guanosine radical cations with water in the gas phase are exclusively initiated by hydration of the radical cations as reported in recent work (Y. Sun et al., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2018, 20, 27510). As gas-phase hydration reactions closely mimic the actual scenario for guanine radical cations in double-stranded DNA, exploration of subsequent reactions within their water complexes can provide an insight into the resulting oxidative damage to nucleosides. Herein guided-ion beam mass spectrometry experiment and direct dynamics trajectory simulations were carried out to examine prototype complexes of the 9-methylguanine radical cation with one and two water ligands (i.e., 9MG˙+·(H2O)1–2) in the gas phase, wherein the complexes were activated by collisional activation in the experiment and by thermal excitation at high temperatures in the simulations. Guided by mass spectroscopic measurements, trajectory results and reaction potential energy surface, three reaction pathways were identified. The first two reaction pathways start with H-atom abstraction from water by the O6 and N7 atoms in 9MG˙+ and are referred to as HAO6 and HAN7, respectively. The primary products of HAO6 and HAN7 reactions, including [9MG + HO6]+/[9MG + HN7]+ and ˙OH, react further to either form [8OH-9MG + HO6]˙+ and [8OH-9MG + HN7]˙+via C8-hydroxylation or form radical cations of 6-enol-guanine (6-enol-G˙+) and 7H-guanine (7HG˙+) via SN2-type methanol elimination. The third reaction pathway corresponds to the formation of 8OH-9MG+ by H elimination from the complex, referred to as HE. Among these product channels, [8OH-9MG + HN7]˙+ has the most favorable formation probability, especially in the presence of additional water molecules. This product may serve as a preceding structure to the 8-oxo-7,8-dihydroguanine lesion in DNA and has implications for health effects of radiation exposure and radiation therapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...