Amphiphilic fluorescent probe self-encored in plasma to detect pH fluctuations in cancer cell membranes†
Abstract
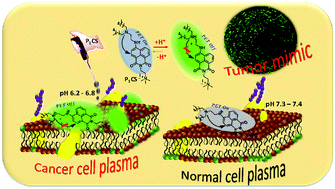
We have developed an amphiphilic pH probe (P1CS) to detect pH levels in the plasma membrane in cancer cells. An elevated fluorescence signal at 550 nm at the cell surface of cancer cells (MDA-MB-231, HeLa cells) prompted the application of P1CS as a pH marker for the cancer cell surface, discriminating it from normal cells (WI-38). Moreover, the probe enables labeling of the surface of multilayered tumor spheroids, which promotes its use as a marker for the surface of tumor tissue.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...