Investigation of the enhanced ability of bile salt surfactants to solubilize phospholipid bilayers and form mixed micelles†
Abstract
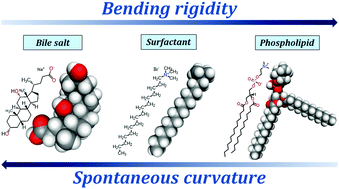
The self-assembly in mixtures of the anionic bile salt surfactant sodium deoxycholate (NaDC) and the zwitterionic phospholipid 1,2-dimyristoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DMPC) in physiological saline solution has been investigated using light scattering, small-angle X-ray scattering and cryo-transmission electron microscopy. Rather small tri-axial ellipsoidal NaDC–DMPC mixed micelles form at a high content of bile salt in the mixture, which increase in size as an increasing amount of DMPC is incorporated into the micelles. Eventually, the micelles begin to grow substantially in length to form long wormlike micelles. At higher mole fractions of DMPC, the samples become turbid and cryo-TEM measurements reveal the existence of large perforated vesicles (stomatosomes), coexisting with geometrically open disks. To our knowledge, stomatosomes have not been observed before for any bile salt–phospholipid system. Mixed micelles are found to be the sole aggregate structure in a very wide regime of bile salt–phospholipid compositions, i.e. up to about 77 mol% phospholipid in the micelles. This is much higher than the corresponding value of 25 mol% observed for the conventional surfactant hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) mixed with DMPC in the same solvent. The enhanced ability of bile salt surfactants to solubilize phospholipid bilayers and form mixed micelles is rationalized using bending elasticity theory. From our theoretical analysis, we are able to conclude that amphiphilic molecules rank in the following order of increasing spontaneous curvature: phospholipids < conventional surfactants < bile salts. The bending rigidity of the different amphiphilic molecules increases according to the following sequence: bile salts < conventional surfactants < phospholipids.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...