Multiple valence electron detachment following Auger decay of inner-shell vacancies in gas-phase DNA
Abstract
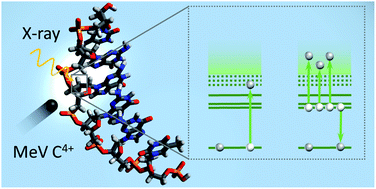
We have studied soft X-ray photoabsorption in the doubly deprotonated gas-phase oligonucleotide [dTGGGGT–2H]2−. The dominating decay mechanism of the X-ray induced inner shell vacancy was found to be Auger decay with detachment of at least three electrons, leading to charge reversal of the anionic precursor and the formation of positively charged photofragment ions. The same process is observed in heavy ion (12 MeV C4+) collisions with [dTGGGGT–2H]2− where inner shell vacancies are generated as well, but with smaller probability. Auger decay of a single K-vacancy in DNA, followed by detachment of three or more low energy electrons instead of a single high energy electron has profound implications for DNA damage and damage modelling. The production of three low kinetic energy electrons with short mean free path instead of one high kinetic energy electron with long mean free path implies that electron-induced DNA damage will be much more localized around the initial K-shell vacancy. The fragmentation channels, triggered by triple electron detachment Auger decay are predominantly related to protonated guanine base loss and even loss of protonated guanine dimers is tentatively observed. The fragmentation is not a consequence of the initial K-shell vacancy but purely due to multiple detachment of valence electrons, as a very similar positive ion fragmentation pattern is observed in femtosecond laser-induced dissociation experiments.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...