Synthesis and biological evaluation of indazole derivatives as anti-cancer agents†
Abstract
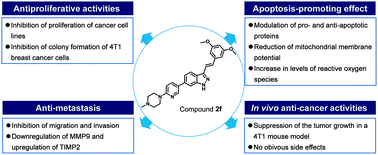
Several FDA approved small molecule anti-cancer drugs contain indazole scaffolds. Here, we report the design, synthesis and biological evaluation of a series of indazole derivatives. In vitro antiproliferative activity screening showed that compound 2f had potent growth inhibitory activity against several cancer cell lines (IC50 = 0.23–1.15 μM). Treatment of the breast cancer cell line 4T1 with 2f inhibited cell proliferation and colony formation. 2f dose-dependently promoted the apoptosis of 4T1 cells, which was connected with the upregulation of cleaved caspase-3 and Bax, and downregulation of Bcl-2. 2f also decreased the mitochondrial membrane potential and increased the levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in 4T1 cells. Additionally, treatment with 2f disrupted 4T1 cells migration and invasion, and the reduction of matrix metalloproteinase metalloproteinase-9 (MMP9) and increase of tissue inhibitor matrix metalloproteinase 2 (TIMP2) were also observed. Moreover, 2f could suppress the growth of the 4T1 tumor model without obvious side effects in vivo. Taken together, these results identified 2f as a potential small molecule anti-cancer agent.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...