Metal ion size profoundly affects H3glyox chelate chemistry†
Abstract
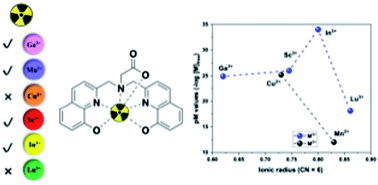
The bisoxine hexadentate chelating ligand, H3glyox was investigated for its affinity for Mn2+, Cu2+ and Lu3+ ions; all three metal ions are relevant with applications in nuclear medicine and medicinal inorganic chemistry. The aqueous coordination chemistry and thermodynamic stability of all three metal complexes were thoroughly investigated by detailed DFT structure calculations and stability constant determination, by employing UV in-batch spectrophotometric titrations, giving pM values (pM = −log[Mn+]free when [Mn+] = 1 μM, [L] = 10 μM at pH 7.4 and 25 °C) – pCu (25.2) > pLu (18.1) > pMn (12.0). DFT calculated structures revealed different geometries and coordination preferences of the three metal ions; notable was an inner sphere water molecule in the Mn2+ complex. H3glyox labels [52gMn]Mn2+, [64Cu]Cu2+ and [177Lu]Lu3+ at ambient conditions with apparent molar activities of 40 MBq μmol−1, 500 MBq μmol−1 and 25 GBq μmol−1, respectively. Collectively, these initial investigations provide insight into the effects of metal ion size and charge on the chelation with the hexadentate H3glyox and indicate that further investigations of the Mn2+–H3glyox complex in 52g/55Mn-based bimodal imaging might be worthwhile.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...