Synthesis and theoretical calculations of metal-antibiotic chelation with thiamphenicol: in vitro DNA and HSA binding, molecular docking, and cytotoxicity studies†
Abstract
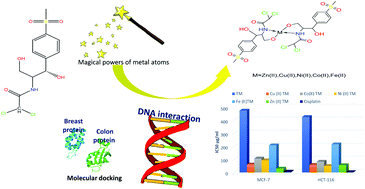
Thiamphenicol (TM) is an antimicrobial drug and a methyl-sulfonyl analogue of chloramphenicol. New metal complexes of TM with Zn(II), Cu(II), Ni(II), Co(II) and Fe(II) were synthesized and characterized using elemental analyses, infrared (IR) and proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-NMR), magnetic susceptibility, electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectroscopy, and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). The IR spectra revealed coordination of the deprotonated ligand to the metal through one oxygen and the nitrogen atom of the amide group. Moreover, EPR analysis of the Cu(II) solid sample indicated a distorted tetrahedral structure with a negligible exchange interaction between the Cu(II) ions. The UV-vis spectral results from the Co(II) and Fe(II) complexes showed a distorted tetrahedral geometric arrangement for both compounds. The DFT calculation approach was used to study the nature of the interaction between the metal ions and the ligand where the molecular stability and bond strengths were evaluated by Natural Bond Orbital (NBO) and quantum parameters. The biological activity of the metal complexes was investigated by several different bioassays. The DNA binding constant Kb showed an intercalation binding mode for both the free drug and the metal compounds. An in vitro protein (HSA) binding study showed binding with TM–Zn Kb = 9.87 × 105 M−1. The cytotoxic activity of each divalent complex was tested against two cell lines: (1) a human colon carcinoma (HCT-116) cell line and (2) a human breast carcinoma (MCF-7) tumor cell line and demonstrated anti-cancer cell activities. Molecular docking was utilized to explain the biological inhibition of the Cu(II) and Zn(II) complexes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...