Mixed fatty acid-phospholipid protocell networks†
Abstract
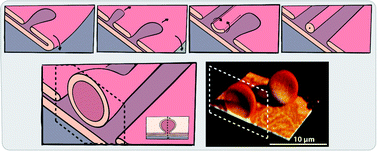
Self-assembled membranes composed of both fatty acids and phospholipids are permeable for solutes and structurally stable, which was likely an advantageous combination for the development of primitive cells on the early Earth. Here we report on the solid surface-assisted formation of primitive mixed-surfactant membrane compartments, i.e. model protocells, from multilamellar lipid reservoirs composed of different ratios of fatty acids and phospholipids. Similar to the previously discovered enhancement of model protocell formation on solid substrates, we achieve spontaneous multi-step self-transformation of mixed surfactant reservoirs into closed surfactant containers, interconnected via nanotube networks. Some of the fatty acid-containing compartments in the networks exhibit colony-like growth. We demonstrate that the compartments generated from fatty acid-containing phospholipid membranes feature increased permeability coefficients for molecules in the ambient solution, for fluorescein up to 7 × 10−6 cm s−1 and for RNA up to 3.5 × 10−6 cm s−1. Our findings indicate that surface-assisted autonomous protocell formation and development, starting from mixed amphiphiles, is a plausible scenario for the early stages of the emergence of primitive cells.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...