Quasi-2D Co3O4 nanoflakes as an efficient gas sensor versus alcohol VOCs†
Abstract
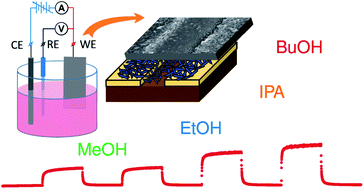
Here, we study quasi-two-dimensional crystals of Co3O4 grown by electrochemical synthesis on Pt electrodes with a nanoflake morphology to serve as a gas sensor. When synthesizing in aqueous electrolytes under applied electrical bias, the material follows a self-hierarchical architecture to primarily appear as the hexagonal nanoflakes α-Co(OH)2. After heating up to 300 °C in air, the as-synthesized material transforms to Co3O4, preserving the original hierarchical morphology. The Co3O4 nanoflakes have been found to have remarkable chemiresistive response when exposed to various kinds of alcohol vapors, at low ppm concentrations in a mixture with air, over a wide range of temperatures up to 300 °C with a detection limit down to the ppb range with direct dependence on the molecule weight of the alcohol. We explain the observed features of the gas response of the Co3O4 nanoflakes by a shift in the electron density under the chemisorption of VOCs, verified by DFT calculations.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...