Stimuli responsive Janus microgels with convertible hydrophilicity for controlled emulsion destabilization†
Abstract
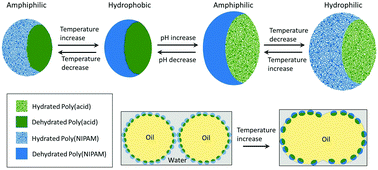
Although the utilization of rigid particles can afford stable emulsions, some applications require eventual emulsion destabilization to release contents captured in the particle-covered droplet. This destabilizing effect is achieved when using stabilizers that respond to controlled changes in environment. Microgels can be synthesized as stimuli responsive polymeric gel networks that adsorb to oil/water interfaces and stabilize emulsions. These particles are commonly hydrogels that swell and collapse in water in response to environmental changes. However, amphiphilic functionality is desired to enhance the adsorption abilities of these hydrogels while maintaining their stimuli responsivity. Microfluidic techniques are used to synthesize Janus microgels with two opposing stimuli responsive hemispheres. The particles have a temperature responsive domain connected to a pH responsive network where each side changes its hydrophilicity in response to a change in temperature or pH, respectively. The Janus microgels are amphiphilic in acidic conditions at 19 °C and alkaline conditions at 40 °C, while the opposite conditions cause a reduction of the amphiphilicity. By stabilizing emulsions with these dual responsive microgels, “smart” droplets that respond to environmental cues are formed. Emulsion droplets remain stable with smaller diameters when aqueous solution conditions favor amphiphilic particles yet, coalesce to larger droplets upon changing pH or temperature. These responsive Janus microgels represent the advancing technology of responsive droplets and demonstrate the applicability of microgels as emulsion stabilizers.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...