Cathodic NH4+ leaching of nitrogen impurities in CoMo thin-film electrodes in aqueous acidic solutions†
Abstract
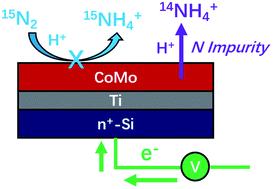
Electrocatalytic reduction of dinitrogen (N2) to ammonium (NH4+) in acidic aqueous solutions was investigated at ambient temperature and pressure using a cobalt–molybdenum (CoMo) thin-film electrode prepared by magnetron reactive sputtering. Increased concentrations of ammonium ions (NH4+) were consistently detected in the electrolyte using ion chromatography (IC) after constant-potential electrolysis at various potentials (≤−0.29 V vs. RHE). Using a newly developed analytical method based on ammonia derivatization, performing the experiments with 15N2-labelled gas led however to the detection of increased 14NH4+ concentrations instead of 15NH4+. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic (XPS) analysis of the electrode surface revealed the presence of Mo![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) N and Mo–NHx species. Several contamination sources were identified that led to substantial increases in the concentration of ammonium ions, including 15NH3 impurities in 15N2 gas. The observed ammonium concentrations can be consistently ascribed to leaching of nitrogen (14N) impurities incorporated in the CoMo film during the sputtering process. Researchers in the field are therefore urged to adopt extended protocols to identify and eliminate sources of ammonia contamination and to very carefully monitor the ammonium concentrations in each experimental step.
N and Mo–NHx species. Several contamination sources were identified that led to substantial increases in the concentration of ammonium ions, including 15NH3 impurities in 15N2 gas. The observed ammonium concentrations can be consistently ascribed to leaching of nitrogen (14N) impurities incorporated in the CoMo film during the sputtering process. Researchers in the field are therefore urged to adopt extended protocols to identify and eliminate sources of ammonia contamination and to very carefully monitor the ammonium concentrations in each experimental step.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...