Dynamic interaction of fluoroquinolones with magnesium ions monitored using bacterial outer membrane nanopores†
Abstract
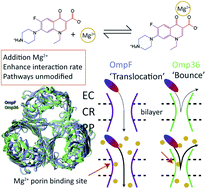
Divalent ions are known to have a severe effect on the translocation of several antibiotic molecules into (pathogenic) bacteria. In the present study we have investigated the effect of divalent ions on the permeability of norfloxacin across the major outer membrane channels from E. coli (OmpF and OmpC) and E. aerogenes (Omp35 and Omp36) at the single channel level. To understand the rate limiting steps in permeation, we reconstituted single porins into planar lipid bilayers and analyzed the ion current fluctuations caused in the presence of norfloxacin. Moreover, to obtain an atomistic view, we complemented the experiments with millisecond-long free energy calculations based on temperature-accelerated Brownian dynamics simulations to identify the most probable permeation pathways of the antibiotics through the respective pores. Both, the experimental analysis and the computational modelling, suggest that norfloxacin is able to permeate through the larger porins, i.e., OmpF, OmpC, and Omp35, whereas it only binds to the slightly narrower porin Omp36. Moreover, divalent ions can bind to negatively charged residues inside the porin, reversing the ion selectivity of the pore. In addition, the divalent ions can chelate with the fluoroquinolone molecules and alter their physicochemical properties. The results suggest that the conjugation with either pores or molecules must break when the antibiotic molecules pass the lumen of the porin, with the conjugation to the antibiotic being more stable than that to the respective pore. In general, the permeation or binding process of fluoroquinolones in porins occurs irrespective of the presence of divalent ions, but the presence of divalent ions can vary the kinetics significantly. Thus, a detailed investigation of the interplay of divalent ions with antibiotics and pores is of key importance in developing new antimicrobial drugs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...