Polyamide monomers via carbonate-promoted C–H carboxylation of furfurylamine†
Abstract
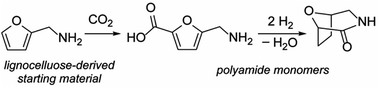
Inedible biomass (lignocellulose) is a largely untapped resource for polymer production because it is synthetically challenging to convert to useful monomers. Here we describe streamlined syntheses of two polyamide monomers from furfurylamine, one of very few chemicals made industrially from lignocellulose. Using carbonate-promoted C–H carboxylation, furfurylamine is converted into a furan-containing amino acid and a tetrahydrofuran-containing bicyclic lactam in two and four steps, respectively. Our syntheses avoid the use of protecting groups and multiple stoichiometric organic reagents required by previous, longer routes to these targets. This work facilitates access to furan- and tetrahydrofuran-based polyamides, which are unavailable from petrochemical feedstocks.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...