Preparation of functionalized poly(1-butene) from 1,2-polybutadiene via sequential thiol-ene click reaction and ring-opening polymerization
Abstract
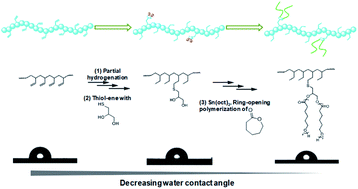
Poly(1-butene) is a kind of unique poly(α-olefin) material that displays exceptional creep resistance and environmental stress cracking resistance, and therefore currently finds wide application in the fields of packaging, films, pipes, etc. However, very few current researchers are paying attention to functional poly(1-butene) despite its great research significance, perhaps due to the general paucity of catalytic systems for synthesizing this material. Therefore, in the present study, we set out to develop an alternative method to prepare polar poly(1-butene)s. Specifically, 1,2-enriched poly(1,3-butadiene), used as a starting material, was partially hydrogenated to afford a quasi-poly(1-butene) polymer containing C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C double bonds. These double bonds were further modified by subjecting the quasi-poly(1-butene) polymer to a thiol-ene reaction in the presence of thiol compounds, and a series of polar poly(1-butene)s that bore significantly improved surface properties were obtained. By using hydroxyl-containing thiol compounds, ring-opening polymerization (ROP) of ε-caprolactone was further implemented. Here, polar poly(ε-caprolactone) was incorporated as side chains, and we were able to control the chain length by adjusting the feeding ratio. The water contact angles of the resultant polymers, i.e., those containing the poly(ε-caprolactone) side chains, were as low as 59.4°, indicating a greater hydrophilicity resulting from the incorporation of these side chains.
C double bonds. These double bonds were further modified by subjecting the quasi-poly(1-butene) polymer to a thiol-ene reaction in the presence of thiol compounds, and a series of polar poly(1-butene)s that bore significantly improved surface properties were obtained. By using hydroxyl-containing thiol compounds, ring-opening polymerization (ROP) of ε-caprolactone was further implemented. Here, polar poly(ε-caprolactone) was incorporated as side chains, and we were able to control the chain length by adjusting the feeding ratio. The water contact angles of the resultant polymers, i.e., those containing the poly(ε-caprolactone) side chains, were as low as 59.4°, indicating a greater hydrophilicity resulting from the incorporation of these side chains.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...