Experimental and theoretical studies on the thermal decomposition of trans-1-chloro-3,3,3-trifluoropropene and 2-chloro-3,3,3-trifluoropropene and their fire-extinguishing performance†
Abstract
trans-1-Chloro-3,3,3-trifluoropropene (trans-CF3CH![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CHCl) and 2-chloro-3,3,3-trifluoropropene (CF3CCl
CHCl) and 2-chloro-3,3,3-trifluoropropene (CF3CCl![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2) have the potential to act as fire extinguishing agents, but their thermal decomposition mechanism and fire extinguishing performance have not been investigated. In this paper, thermal decomposition experiments and theoretical calculations were carried out to verify the possible thermal decomposition process and fire extinguishing performance of these potential fire extinguishing agents. trans-CF3CH
CH2) have the potential to act as fire extinguishing agents, but their thermal decomposition mechanism and fire extinguishing performance have not been investigated. In this paper, thermal decomposition experiments and theoretical calculations were carried out to verify the possible thermal decomposition process and fire extinguishing performance of these potential fire extinguishing agents. trans-CF3CH![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CHCl and CF3CCl
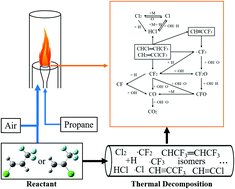
CHCl and CF3CCl![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2 can be decomposed into radicals, such as HCl, ˙CF3, and ˙CF2, which can consume ˙OH and ˙H radicals for fire suppression. Furthermore, the experimental and calculation results demonstrated that CF3CCl
CH2 can be decomposed into radicals, such as HCl, ˙CF3, and ˙CF2, which can consume ˙OH and ˙H radicals for fire suppression. Furthermore, the experimental and calculation results demonstrated that CF3CCl![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2 shows better thermal stability. To characterize the inhibitory efficiency of trans-CF3CH
CH2 shows better thermal stability. To characterize the inhibitory efficiency of trans-CF3CH![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CHCl and CF3CCl
CHCl and CF3CCl![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2, the minimum extinguishing concentrations were measured to be 6.8% and 6.9%, respectively. As a result, trans-CF3CH
CH2, the minimum extinguishing concentrations were measured to be 6.8% and 6.9%, respectively. As a result, trans-CF3CH![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CHCl and CF3CCl
CHCl and CF3CCl![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2 performed well, and their application as Halon substitutes is worth exploring.
CH2 performed well, and their application as Halon substitutes is worth exploring.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...