Palladium(ii) complexes of tetradentate donor–acceptor Schiff base ligands: synthesis and spectral, structural, thermal and NLO properties†
Abstract
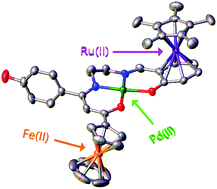
This report explores the synthesis and spectral, structural, thermal, electrochemical, linear and nonlinear (NLO) properties of unsymmetrically-substituted N2O2 tetradentate Schiff base proligand and related bi and trimetallic PdII complexes. The diprotic proligand Fc-C(![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O)CH
O)CH![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C(4-C6H4OH)NH-CH2CH2N
C(4-C6H4OH)NH-CH2CH2N![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH-(2-OH,4-CO2H-C6H3) (2, Fc = ferrocenyl = (η5-C5H5)Fe(η5-C5H4))), is synthetized by condensation of the 4-hydroxyphenyl-appended ferrocenylenaminone 1 with 4-formyl-3-hydroxybenzoic acid. The related Pd(II) complexes, neutral bimetallic 3 and ionic trimetallic 4, were both prepared via a three-component one-pot template reaction involving the half unit 1, palladium acetate, the CO2H-functionalized salicylaldehyde and the organometallic salicylaldehyde [Cp*Ru(η6-2-OH-C6H4CHO)]PF6, respectively (Cp* = η5-C5Me5). Compounds 2–4 were isolated as colored air and thermally stable solids in 74–86% yields. They were thoroughly characterized using various physicochemical tools, such as CHN analyses, IR, UV-vis, 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopy, TGA and cyclic voltammetry. The molecular structures of 3 and 4 were authenticated by single-crystal X-ray diffraction methods. In both 3 and 4, the four-coordinate palladium atom adopts a square planar geometry with two nitrogen and two oxygen atoms as donors occupying cis positions. Additionally in 4, the ferrocenyl and Cp*Ru+ moieties exhibit an anti-conformation with respect to the [Pd(N2O2] Schiff base platform. The electrochemical behavior of the two Pd(II) complexes was investigated by cyclic voltammetry, showing in both cases a reversible redox process ascribed to the Fe(II)/Fe(III) couple of the dangling donor ferrocene. Compared to that for 3, the oxidation wave for 4 is anodically shifted by 30 mV, evidencing a greater electron accepting ability of Cp*Ru+vs. –CO2H. The second-order NLO responses of the push–pull derivatives 2–4 have been determined by harmonic light scattering measurements in N,N-dimethylformamide solutions at 1.91 μm incident wavelength, and rather good quadratic hyperpolarisability β values ranging from 120–160 × 10−30 esu were determined.
CH-(2-OH,4-CO2H-C6H3) (2, Fc = ferrocenyl = (η5-C5H5)Fe(η5-C5H4))), is synthetized by condensation of the 4-hydroxyphenyl-appended ferrocenylenaminone 1 with 4-formyl-3-hydroxybenzoic acid. The related Pd(II) complexes, neutral bimetallic 3 and ionic trimetallic 4, were both prepared via a three-component one-pot template reaction involving the half unit 1, palladium acetate, the CO2H-functionalized salicylaldehyde and the organometallic salicylaldehyde [Cp*Ru(η6-2-OH-C6H4CHO)]PF6, respectively (Cp* = η5-C5Me5). Compounds 2–4 were isolated as colored air and thermally stable solids in 74–86% yields. They were thoroughly characterized using various physicochemical tools, such as CHN analyses, IR, UV-vis, 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopy, TGA and cyclic voltammetry. The molecular structures of 3 and 4 were authenticated by single-crystal X-ray diffraction methods. In both 3 and 4, the four-coordinate palladium atom adopts a square planar geometry with two nitrogen and two oxygen atoms as donors occupying cis positions. Additionally in 4, the ferrocenyl and Cp*Ru+ moieties exhibit an anti-conformation with respect to the [Pd(N2O2] Schiff base platform. The electrochemical behavior of the two Pd(II) complexes was investigated by cyclic voltammetry, showing in both cases a reversible redox process ascribed to the Fe(II)/Fe(III) couple of the dangling donor ferrocene. Compared to that for 3, the oxidation wave for 4 is anodically shifted by 30 mV, evidencing a greater electron accepting ability of Cp*Ru+vs. –CO2H. The second-order NLO responses of the push–pull derivatives 2–4 have been determined by harmonic light scattering measurements in N,N-dimethylformamide solutions at 1.91 μm incident wavelength, and rather good quadratic hyperpolarisability β values ranging from 120–160 × 10−30 esu were determined.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...