Synthesis and characterization of bis(dithiafulvenyl)-substituted fluorenones and fluorenylidene-1,3-dithioles†
Abstract
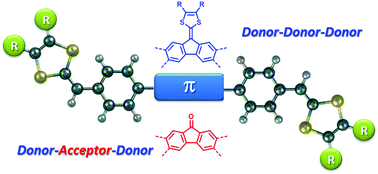
This work reports the synthesis and characterization of a series of π-conjugated donor/acceptor (D/A) molecular systems, in which redox-active dithiafulvenyl (DTF) end groups are covalently linked to electron-accepting fluorenones or electron-donating fluorenylidene-1,3-dithioles through phenylene bridges. Structurally, the central π-units of these D/A systems adopt 2,7- (linear) and 3,6-disubstituion (wedge-shaped) patterns and their electronic nature can be divided into D–A–D and D–D–D types. The molecular structural and electronic properties of these compounds were investigated by using single crystal X-ray diffraction (XRD) and UV-vis absorption analyses, in conjunction with density functional theory (DFT) calculations. Their electrochemical redox properties were examined by cyclic voltammetric (CV) analysis. Our studies showed that the DTF end groups in these compounds can undergo oxidative coupling reactions under electrochemical conditions to form polymeric products with varied redox activities. The electronic nature of the central π-unit, the substitution pattern, and the pendant alkyl group have been found to significantly influence the electronic absorption, redox properties, and electrochemical reactivities of these D/A molecular systems.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...