The adsorption and growth of Agn (n = 1–4) clusters on cubic, monoclinic, and tetragonal ZrO2 surfaces: a first-principles study†
Abstract
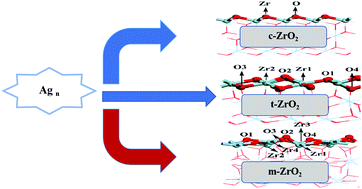
Supported metal nanoparticles are widely used as catalysts in the industrial production of chemicals, but still suffer from deactivation because of metal leaching and sintering at high temperature. In this work, the adsorption and growth of Agn (n = 1–4) on cubic zirconia (c-ZrO2) (1 1 1), monoclinic zirconia (m-ZrO2) (![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) 1 1), and tetragonal zirconia (t-ZrO2) (1 0 1) surfaces has been examined with the aid of first-principles calculations and the periodic supercell model. The results show that the adsorption of a single silver atom on different zirconia surfaces follows the trend t-ZrO2(1 0 1) > m-ZrO2(
1 1), and tetragonal zirconia (t-ZrO2) (1 0 1) surfaces has been examined with the aid of first-principles calculations and the periodic supercell model. The results show that the adsorption of a single silver atom on different zirconia surfaces follows the trend t-ZrO2(1 0 1) > m-ZrO2(![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) 1 1) > c-ZrO2(1 1 1). The growth of Agn (n = 2–4) on different zirconia surfaces is thermodynamically feasible and the supports can improve the dispersion of the silver particles, especially the surface of t-ZrO2(1 0 1). Bader charge analysis was conducted on the most stable adsorption structure of the different zirconia surfaces for a single silver atom. The results show that no major charge transfer was observed when the silver atoms adsorbed on the stoichiometric c-ZrO2(1 1 1), t-ZrO2(1 0 1) and m-ZrO2(
1 1) > c-ZrO2(1 1 1). The growth of Agn (n = 2–4) on different zirconia surfaces is thermodynamically feasible and the supports can improve the dispersion of the silver particles, especially the surface of t-ZrO2(1 0 1). Bader charge analysis was conducted on the most stable adsorption structure of the different zirconia surfaces for a single silver atom. The results show that no major charge transfer was observed when the silver atoms adsorbed on the stoichiometric c-ZrO2(1 1 1), t-ZrO2(1 0 1) and m-ZrO2(![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) 1 1) surfaces, and the silver's unpaired electron remains largely localized on the metal adatom upon adsorption. These findings could help in understanding the metal cluster–support interactions and designing new catalysts for this kind of reaction.
1 1) surfaces, and the silver's unpaired electron remains largely localized on the metal adatom upon adsorption. These findings could help in understanding the metal cluster–support interactions and designing new catalysts for this kind of reaction.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...