Photo-rechargeable fuel cell using photo-hydrogenation reactions of quinone molecules†
Abstract
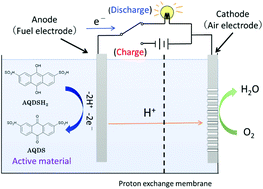
We demonstrated a new concept of a photo-rechargeable fuel cell using the protonation and de-protonation reactions of quinone molecules. It was found that disodium 9,10-anthraquinone-2,7-disulfonate (AQDS) can work as active quinone molecules for the proposed cell. Photo-induced protonation reaction of AQDS, confirmed by UV-vis measurements, corresponds to the charge process of the proposed photo-rechargeable cell and the protonated AQDS electrode can work just like the fuel electrode of a conventional fuel cell. It was revealed by full-cell experiments that this photo-rechargeable fuel cell works practically.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...