Controlling the distribution of nanoparticles in hydrogels via interfacial synthesis†
Abstract
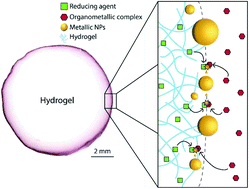
In this article, a dual-solvent method is presented which allows for precise control over the distribution of nanoparticles (NPs) in hydrogels. The technique is based on the interfacial reaction between a reducing agent (herein THPC) initially solubilized in the hydrogel phase, and an organometallic precursor (herein Au(PPh3)Cl) solubilized in the surrounding organic liquid phase. When the organic phase is completely immiscible with water, the interfacial reaction yields a fragile monolayer film of NPs at the hydrogel surface. Then, the addition of a co-solvent (miscible with both aqueous and organic phases) allows precise tuning over the distribution of NPs, from a fine and well-anchored layer at the interface, to the whole gel volume. As a result, it is possible to independently control the size and concentration of NPs, and their distribution. The impact of such control is demonstrated with the reduction of p-nitrophenol to p-aminophenol catalyzed by gold nanoparticles (AuNPs). When AuNPs are mostly localized at the gel surface, the apparent reaction rate is more than 10× superior compared to AuNPs distributed in the whole gel – at comparable particle content and size. This approach is straightforward, decisive and compatible with broad arrays of NPs and hydrogel chemistries, and solvent combinations.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...