The prophylactic effects of different Lactobacilli on collagen-induced arthritis in rats†
Abstract
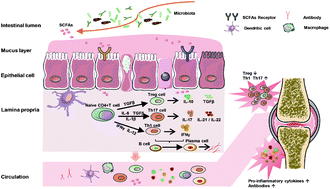
Recent studies have shed light on the prophylactic effects of Lactobacilli on rheumatoid arthritis (RA). However, the modulatory mechanisms of Lactobacilli remain unclear. The current study evaluated different Lactobacillus species’ ability to alleviate arthritis induced by collagen. Rats were intragastrically administered different lactobacilli cocktails two weeks before arthritis induction. The results revealed that the performance of Lactobacillus in relieving arthritis was different for some species. L. reuteri, L. casei, L. rhamnosus and L. fermentum attenuated RA through species-independent pathways that inhibited pro-inflammatory cytokines and anti-CII-antibodies; and through species-dependent immune regulation that was based on rebalancing the intestinal microbiota, and metabolites such as short-chain fatty acids. In particular, L. reuteri and L. casei weaken the Th1 immune response, while L. rhamnosus and L. fermentum impaired Th17 responses. Interestingly, L. plantarum did not alleviate arthritis although it did suppress Th1 and Th17 immune responses, while L. salivarius only delayed the onset of arthritis without influencing the immune response. In conclusion, Lactobacilli protect against collagen-induced-arthritis through both common and individual pathways.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...