Gut microbiota mediate the protective effects on endometritis induced by Staphylococcus aureus in mice†
Abstract
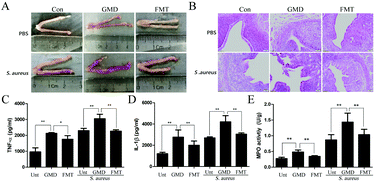
Endometritis, the inflammation of the endometrial lining caused by bacterial pathogens, is associated with reproductive failure. Recent studies have shown that gut microbiota play an important role in infectious diseases. However, the roles of the gut microbiota in endometritis remain unclear. Here, we assessed the effects and mechanisms of the gut microbiota during endometritis induced by Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus). A mouse gut microbiota-dysbiosis model was established by a mixture of antibiotics (Abx) and subsequently, a model of endometritis was established by the uterine perfusion of S. aureus. Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) was performed to evaluate the relationship between gut microbiota and endometritis. The results showed that the mice with gut microbiota-dysbiosis developed uterine inflammation, while this inflammatory response of the uterus was alleviated in mice with FMT to gut microbiota-dysbiosis. In addition, S. aureus-induced endometritis was greater in severity in the mice with gut dysbiosis as compared to the untreated mice. Moreover, these effects were reversed in mice with FMT to the gut microbiota-dysbiosis. GC-MS analysis demonstrated that the levels of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) in the feces of mice with gut microbiota-dysbiosis significantly decreased and pretreatment with sodium butyrate or sodium propionate increased the concentrations of butyrate or propionate in both the circulation and uterine tissues, thereby reducing the severity of endometritis induced by S. aureus. In addition, the increased pathogen load in the uteri of the mice with gut microbiota-dysbiosis was associated with a reduction in the phagocytic ability and responsiveness of neutrophils. In conclusion, the gut microbiota offer a protective effect against S. aureus-induced endometritis by regulating the levels of SCFAs and maintaining the phagocytic ability and responsiveness of neutrophils.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...