Comparisons of protective effects between two sea cucumber hydrolysates against diet induced hyperuricemia and renal inflammation in mice†
Abstract
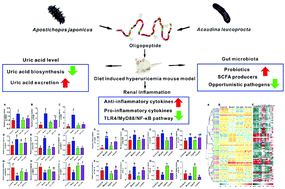
Hyperuricemia is an important risk factor for many diseases including hypertension and type 2 diabetes. This study investigated and compared the effects of hydrolysates of two sea cucumber species, Apostichopus japonicus and Acaudina leucoprocta, on the alleviation of diet-induced hyperuricemia and renal inflammation. The structure and abundance of oligopeptides in enzymatic hydrolysates of A. japonicus (EH-JAP) and A. leucoprocta (EH-LEU) were identified via MALDI-TOF/TOF-MS, and the anti-hyperuricemic and anti-inflammatory effects of the hydrolysates were explored in a diet-induced hyperuricemic mouse model. Both EH-JAP and EH-LEU inhibit uric acid biosynthesis and promote uric acid excretion, leading to the alleviation of the hyperuricemic phenotype. In addition, these two treatments down-regulated the transcription of pro-inflammatory cytokines, up-regulated the transcription of anti-inflammatory cytokines, and inhibited the activation of the Toll-like receptor 4/myeloid differentiation factor 88/NF-kappaB (TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB) signaling pathway, leading to the alleviation of renal inflammation. EH-JAP had better effects than EH-LEU due to differences in their regulation of uric acid biosynthesis, uric acid excretion and release of anti-inflammatory cytokines. In addition, EH-JAP and EH-LEU treatment alleviated the dysfunction of the gut microbiota by increasing the abundance of beneficial Lactobacillus and short-chain fatty acid producers and decreasing the abundance of opportunistic pathogens. This study provides a valuable reference for the development of sea cucumber applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...