Dietary resveratrol attenuated colitis and modulated gut microbiota in dextran sulfate sodium-treated mice
Abstract
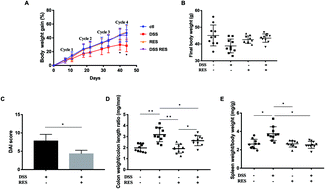
Accumulating evidence suggests that the gut microbiota plays an important role in the pathogenesis of colitis and that its composition could be modulated by exposure to dietary components. Thus, it may be possible to ameliorate the severity of colitis through administration of dietary components. Herein, we determined the effects of orally administered resveratrol on the gut microbiota composition and the resulting inflammatory status of a dextran sodium sulfate (DSS)-induced colitis mouse model. Our results supported our hypothesis that dietary resveratrol altered the microbial composition and restored microbial community diversity in DSS-treated mice. Specifically, resveratrol effectively decreased the abundance of the genera Akkermansia, Dorea, Sutterella and Bilophila, and increased the proportion of Bifidobacterium in colitic mice. Resveratrol was also able to prevent mouse body weight loss, reduce the disease activity index, attenuate tissue damage, and down-regulate the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-2, IFN-γ, GM-CSF, IL-1β, IL-6, KC/GRO, and TNF-α in the colon of DSS-treated mice. Pearson's correlation analysis indicated significant correlations between the relative levels of these pro-inflammatory cytokines and alterations of the gut microbiota. Our results demonstrated that dietary resveratrol attenuated the inflammatory status and alleviated gut microbiota dysbiosis in a colitis mouse model.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...