Liquefied gas electrolytes for wide-temperature lithium metal batteries†
Abstract
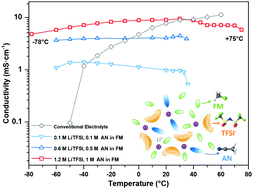
The momentum in developing next-generation high energy batteries calls for an electrolyte that is compatible with both lithium (Li) metal anodes and high-voltage cathodes, and is also capable of providing high power in a wide temperature range. Here, we present a fluoromethane-based liquefied gas electrolyte with acetonitrile cosolvent and a higher, yet practical, salt concentration. The unique solvation structure observed in molecular dynamics simulations and confirmed experimentally shows not only an improved ionic conductivity of 9.0 mS cm−1 at +20 °C but a high Li transference number (tLi+ = 0.72). Excellent conductivity (>4 mS cm−1) was observed from −78 to +75 °C, demonstrating operation above fluoromethane's critical point for the first time. The liquefied gas electrolyte also enables excellent Li metal stability with a high average coulombic efficiency of 99.4% over 200 cycles at the aggressive condition of 3 mA cm−2 and 3 mA h cm−2. Also, dense Li deposition with an ideal Li–substrate contact is seen in the liquefied gas electrolyte, even at −60 °C. Attributed to superior electrolyte properties and the stable interfaces on both cathode and anode, the performances of both Li metal anode and Li/NMC full cell (up to 4.5 V) are well maintained in a wide-temperature range from −60 to +55 °C. This study provides a pathway for wide-temperature electrolyte design to enable high energy density Li–metal battery operation between −60 to +55 °C.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...