Spinel-structured Mn–Ni nanosheets for NH3-SCR of NO with good H2O and SO2 resistance at low temperature
Abstract
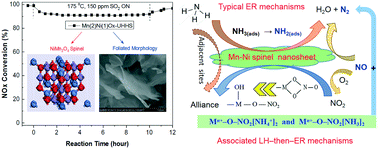
Novel Mn–Ni spinel nanosheets were investigated for the NH3-SCR of NO at low temperature by urea-hydrolysis (UH) and urea-hydrolysis hydrothermal-synthesis (UHHS), and compared with co-precipitation hydrothermal synthesis (CPHS) and co-precipitation (CP) methods. The optimum molar ratio of Mn/Ni (2 : 1) and urea/(Mn + Ni) (3 : 1) were determined, as also were the suitable hydrothermal temperature (130 °C for 24 h) and further calcination (450 °C for 6 h). An Mn(2)Ni(1)Ox-UHHS catalyst produced a purer spinel-structured NiMn2O4 nanosheet than Mn(2)Ni(1)Ox-UH, both of which showed highly efficient SCR activity (>98% NOx conversion at 100–250 °C) and N2 selectivity (>95% at <150 °C and >85% at <250 °C). The NiMn2O4-UHHS nanosheet also exhibited excellent resistance to H2O and SO2 in the low-temperature range (85–90% NOx conversion at 150–300 °C with 10 vol% H2O and 150 ppm SO2). Characterization with BET, TPD, TPR, XPS SEM-EDS, TGA, AXNES and DRIFTS indicated that the main reasons for the excellent activity and resistances were the high specific surface area, greater NH3 adsorption ability and more efficient electronic interaction (Mn3+ + Ni3+ ↔ Mn4+ + Ni2+) of active octahedral-sites in the [Ni2+Mn4+]tet[Ni2+Ni3+Mn3+Mn4+]octO4 spinel structure with an outside configuration of tetrahedrons embedded with Ni which avoided the sulfation of the inside octahedron-wrapped Mn active sites, and the nanosheet morphology which retarded the adhesion of sulfur ammonia species, resulting in the remission of deposition/inhibition effects. The reaction pathways were based on ER mechanisms via gaseous NO with adsorbed NH3-species and also the LH-then-ER mechanisms through the combination of bidentate nitrate with coordinated NH3/NH4+, which were less affected by SO2 competitive adsorption, attributed to be a major reason for good SO2-resistance.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...