On demand production of ethers or alcohols from furfural and HMF by selecting the composition of a Zr/Si catalyst†
Abstract
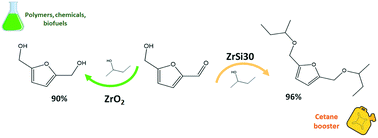
Zr/Si mixed oxides with different amounts of silica (0–50 wt%) were prepared by a simple sol–gel method. These catalysts were tested in a cascade reaction of furfural and 5-hydroxymethyl furfural (HMF) with 2-butanol to form the corresponding alcohols or ethers through a combination of transfer hydrogenation and etherification processes under mild conditions. The selectivity can be finely tuned by changing the silica content which heavily impacts the acid–base properties. On pure ZrO2, featuring acid–base pairs, only the catalytic transfer hydrogenation occurs leading to alcohol products. In contrast, on ZrSi30 the etherification reaction is strongly favored owing to near one-to-one Lewis and Brønsted acid sites. Ethers can thus be produced in high yields (≥90%), in particular the highly valuable diether of 5-hydroxymethyl furfural. The catalysts were characterized by N2 and CO2 absorption isotherms, FT-IR of adsorbed pyridine, 2-propanol TPD, and STEM-EDX mapping. For the first time we show that the tuning of acid–base properties by simple silica addition, with the somewhat unexpected rise of Brønsted acidity, may represent the starting point for the development of cheap but highly active and selective catalysts for furfural and HMF transformation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...