Transformation of γ-valerolactone into 1,4-pentanediol and 2-methyltetrahydrofuran over Zn-promoted Cu/Al2O3 catalysts†
Abstract
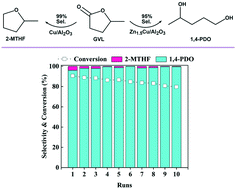
The transformation of γ-valerolactone (GVL) into 1,4-pentanediol (1,4-PDO) and 2-methyltetra-hydrofuran (2-MTHF) in the presence of H2, one of the useful biomass conversion and utilization processes, was investigated with monometallic Cu/Al2O3 and bimetallic ZnCu/Al2O3 catalysts. A 10 wt% Cu-loaded monometallic catalyst produced 1,4-PDO and 2-MTHF in comparable quantities at a medium conversion (∼50%). When Zn was added in a range of Zn/Cu molar ratios of up to 2, in contrast, the catalysts yielded 1,4-PDO in a high selectivity of about 97% at low and high conversion levels. In addition, the 1,4-PDO selectivity over the ZnCu/Al2O3 catalysts remained almost unchanged during recycled runs. That is, the addition of Zn to Cu/Al2O3 switched the product selectivity and improved the catalyst stability and reusability. Furthermore, the physicochemical properties of the catalysts were characterized by several methods including XRD, TEM, TPR, XPS, FTIR of adsorbed pyridine, and so on. On the basis of those results, the relationships between the catalytic performance (activity, selectivity, and reusability) and the catalyst structural features were discussed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...