Polymer fiber membrane-based direct ethanol fuel cell with Ni-doped SnO2 promoted Pd/C catalyst†
Abstract
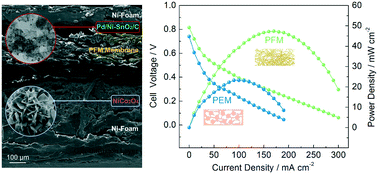
The wide application of direct ethanol fuel cells (DEFCs) was blocked by the sluggish catalytic activity of catalysts, insufficient ionic conductivity of the polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM), and ethanol crossover issues. To overcome the problems mentioned above, a novel DEFC system with a polymer fiber membrane (PFM) and nonplatinum catalysts is proposed. In this system, the performance of the anode catalyst Pd/C is significantly promoted by homogeneous Ni-doped SnO2 nanoparticles, and the inexpensive permeable PFM is used as a substitute for the PEM. Due to the remarkable catalytic activity and the optimized resistance, the PFM-based DEFC exhibits encouraging performance, which can afford a peak power density of 47.4 mW cm−2 with a porous NiCo2O4 cathode catalyst. Moreover, it can operate continuously for 100 h with only 4.56% drop in electrical output. Therefore, this study provides a very effective strategy for optimizing DEFCs with low cost and high performance.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...