A CO2-induced ROCO2Na/ROCO2H buffer solution promoted the carboxylative cyclization of propargyl alcohol to synthesize cyclic carbonates†
Abstract
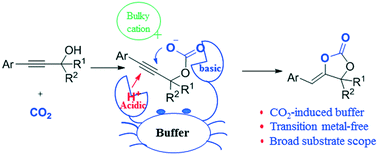
A CO2-induced ROCO2Na/ROCO2H buffer solution is developed and employed in the carboxylative cyclization of propargyl alcohol to generate α-alkylene cyclic carbonates. The introduction of CO2 into the propargyl alcohol/sodium tertiary pentoxide system can provide the ROCO2Na/ROCO2H buffer solution with both basic and acidic species. The basic and acidic species can simultaneously promote the generation of a carbonate anion intermediate and the interaction between the alkyne moieties of propargyl alcohol and protons (H+), facilitating carboxylative cyclization. Furthermore, the bulky (n-C4H9)4N+ cation of tetrabutylammonium bromide as an additive plays a crucial role in enhancing the nucleophilicity of the carbonate anion intermediate. Various α-alkylene cyclic carbonates are obtained in this catalytic system with relatively good yields at 80 °C.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...