Mechanistic investigation of zinc-promoted silylation of phenylacetylene and chlorosilane: a combined experimental and computational study†
Abstract
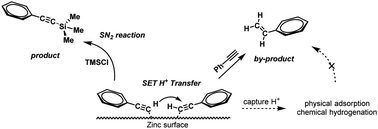
The zinc-promoted silylation method is of great importance to synthesize high-performance silicon-containing arylacetylene (PSA) resins in the industry. However, it is difficult to eliminate the accompanied by-product of terminal alkenes due to the lack of mechanistic understanding of the silylation. The initiation of zinc-promoted silylation is facilitated by the interaction between zinc and phenylacetylene. Our DFT calculations indicated that the intermolecular hydrogen transfer of phenylacetylene follows an ionic pathway, which generates a phenylacetylene anion and the corresponding alkene moieties on the zinc surface. The styrene by-product is observed in this stage, with its alkene moieties desorbing as radicals into the solvent under the high reaction temperature. Three possible intermediates of surface phenylacetylene anions were proposed including PhC![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) C–Zn, PhC
C–Zn, PhC![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) CZnCl, and (PhC
CZnCl, and (PhC![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) C)2Zn. These carbanion–zinc intermediates undergo an SN2 reaction with Me3SiCl to afford the alkynylsilane on the zinc surface, which is calculated to be the rate-determining step for the zinc-promoted silylation reaction.
C)2Zn. These carbanion–zinc intermediates undergo an SN2 reaction with Me3SiCl to afford the alkynylsilane on the zinc surface, which is calculated to be the rate-determining step for the zinc-promoted silylation reaction.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2020 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...