Interactions of water confined in a metal–organic framework as studied by a combined approach of Raman, FTIR, and IR electroabsorption spectroscopies and multivariate curve resolution analysis†
Abstract
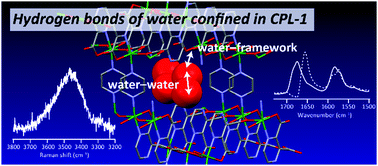
Water in nanoconfinement shows distinct properties that are markedly different from those of bulk water. These unique properties stem not only from the water–water interaction but also from the interactions between water and the surrounding confining environment. Here we used a combined approach of vibrational spectroscopies (Raman, FTIR, and IR electroabsorption) and a multivariate curve resolution technique to study the interactions of water in a heterogeneous confining environment within a prototype of pillared layer-type metal–organic frameworks (MOFs), CPL-1 ([Cu2(pzdc)2(pyz)]n, where pzdc = 2,3-pyrazinedicarboxylate, pyz = pyrazine). The OH stretching Raman spectrum of hydrated CPL-1 microcrystals revealed that the adsorbed water molecules resemble the subpopulation of bulk water whose hydrogen bond is weak. Multivariate curve resolution analysis of FTIR spectra monitoring water desorption from CPL-1 allowed for accurate assignments of the framework's carboxylate vibrational modes associated with water-filled and empty nanopores of the MOF, and for quantitative determination of the number fraction of these pores. Furthermore, building on the assignments so made, IR electroabsorption measurements showed that the hydrogen-bonding interaction with water adsorbed in CPL-1 has little impact on the response to electric fields of the framework vibrational modes. The present findings altogether provide a solid basis of elucidating water confined in CPL-1 and demonstrate the potential of the combined vibrational spectroscopic method for interrogating the interactions within MOFs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...