Probing NaCl hydrate formation from aqueous solutions by terahertz time-domain spectroscopy†
Abstract
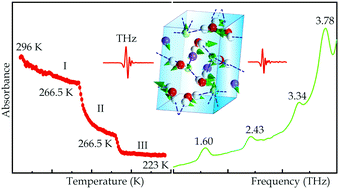
The cooling-induced formation of a hydrate in aqueous NaCl solutions was probed using terahertz time-domain spectroscopy (THz-TDS). It was found that the NaCl hydrate formation is accompanied by the emergence of four new absorption peaks at 1.60, 2.43, 3.34 and 3.78 THz. Combining X-ray diffraction measurements with solid-state based density functional theory (DFT) calculations, we assign the observed terahertz absorption peaks to the vibrational modes of the formed NaCl·2H2O hydrate during cooling. This work shows that THz-TDS based analysis has great potential in studying ionic hydrates and the newly revealed collective vibrational modes could be sensitive indicators to achieve quantitative analysis in phase transitions and lattice dynamics.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...