Characterization of plasma and gas-phase chemistry during boron-nitride nanomaterial synthesis by laser-ablation of boron-rich targets
Abstract
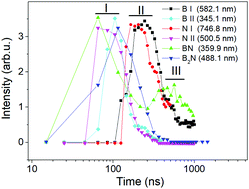
In this work, solid targets made from boron and boron nitride (BN) materials are ablated by a nanosecond pulsed laser at sub-atmospheric pressures of nitrogen and helium gases. The excited species in the ablation plume from the target are probed by spatiotemporally resolved optical emission spectroscopy (OES). The evaluation of the chemical composition of the plasma plume revealed that for both boron-rich targets, emission from BN molecules is always observed in nitrogen-rich environments. In addition, BN molecules are also present when ablating a boron nitride target in a helium gas environment, an indication that BN molecules in the plume may originate from the solid target. Furthermore, the ablation of the BN target features emission of B2N molecules, regardless of the pressure and surrounding gas. These results suggest that the ablation of the BN target is more favorable for the generation of complex molecules containing boron and nitrogen species and possibly hint that BN is also more favorable feedstock for high-yield BN nanomaterial synthesis. Plasma parameters such as the electron temperature (peak value of 1.3 eV) and density (peak value of 2 × 1018 cm−3) were also investigated in this work in order to discuss the chemical dynamics in the plume.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...