Two-dimensional few-layered PC3 as a promising photocatalyst for overall water splitting
Abstract
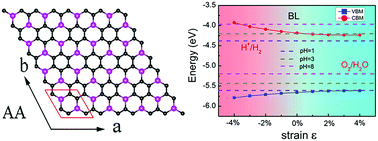
Recently, 2D carbon phosphides (PCs) have attracted much attention due to their superior electronic and photovoltaic properties suitable for potential applications in field effect transistors and photodetectors. In this work, we systematically investigate the stability, electronic properties, optical absorption and photocatalytic water splitting performance of few-layered PC3 by using the first principles calculation method. Numerical results indicate that both monolayered and bilayered PC3 can serve as efficient photocatalysts for overall water splitting due to their high stability, moderate band gaps, suitable band edge positions, anisotropic high carrier mobilities and strong capacity of solar absorption. Compared with monolayered PC3, bilayered PC3 displays higher carrier mobilities (2500–23 000 cm2 V−1 s−1) and a wider optical absorption spectrum. Moreover, by applying an in-plane biaxial strain, the utilization of solar energy and the pH range suitable for overall water splitting can be improved effectively for both monolayered and bilayered PC3. Our work reliably expands the potential application of 2D few-layered PC3 in the field of nano-electronics and nano-optoelectronics.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2020 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...