Responsive agarose hydrogel incorporated with natural humic acid and MnO2 nanoparticles for effective relief of tumor hypoxia and enhanced photo-induced tumor therapy†
Abstract
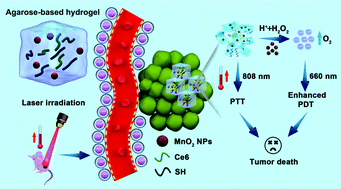
In spite of widespread applications of nano-photosensitizers, poor tumor penetration and severe hypoxia in the tumor microenvironment (TME) always result in an undesirable therapeutic outcome of photodynamic therapy (PDT). Herein, a biocompatible agarose-based hydrogel incorporated with sodium humate (SH), manganese oxide (MnO2) and chlorin e6 (Ce6) was synthesized as agarose@SH/MnO2/Ce6 through a “co-trapped” strategy during a sol–gel process and employed for combined photothermal therapy (PTT) and enhanced PDT. NIR-induced local hyperthermia is responsible for not only activating Ce6 release, but also triggering the catalytic decomposition of H2O2 mediated by MnO2 to relieve hypoxia. Such a hybrid hydrogel can realize deep tissue penetration through intratumoral injection, and exhibit remarkable tumor-site retention. Moreover, programmed laser irradiation led to an extremely high tumor growth inhibition rate of 93.8% in virtue of enhanced PTT/PDT. In addition, ultralow systemic toxicity caused by the hybrid hydrogel was further demonstrated in vivo. This reliable and eco-friendly hydrogel paves the way for the development of smart gel-based biomaterials, which respond to both exogenous and endogenous stimuli, towards the management of cancer and other major diseases.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...