Targeted multifunctional nanomaterials with MRI, chemotherapy and photothermal therapy for the diagnosis and treatment of bladder cancer†
Abstract
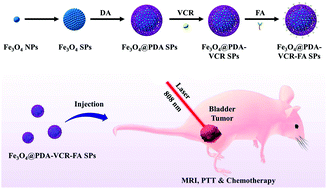
Bladder cancer is a common urinary tract tumor in clinic, and its morbidity and mortality are always high. Surgical treatment is operator dependent, residual tumor cells often lead to tumor recurrence, and chemotherapy after surgery causes high side effects. So, it is urgent to develop new methods for the theranostics of bladder cancer. Among them, functional nanomaterials have shown good application in tumor theranostics, but they are rarely used in bladder cancer. In our work, we demonstrate the fabrication of folate-modified vincristine-loaded polydopamine-coated Fe3O4 superparticles (Fe3O4@PDA-VCR-FA SPs), and applied them in the theranostics of bladder cancer. The PDA shell not only improves the colloidal stability and biocompatibility, but also enhances the photothermal effect and prolongs the blood circulation half-life. The half-life of Fe3O4@PDA-VCR-FA SPs in blood is calculated as 2.83 h, and the tumor retention rate is 5.96 %ID g−1, these data are significantly higher than those before folic acid modification. The superparamagnetism of Fe3O4 and loading of vincristine endow Fe3O4@PDA-VCR-FA SPs with magnetic resonance imaging and chemotherapy capabilities. Further by employing NIR laser-triggered photothermal therapy, bladder tumors were ablated completely, and no recurrence was observed. Blood and histological tests of the major organs confirm that Fe3O4@PDA-VCR-FA SPs show good biosafety.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...