Nanoplasmonic sensor array for the detection and discrimination of pesticide residues in citrus fruits†
Abstract
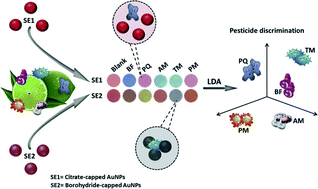
Great attention has been directed towards developing rapid and straightforward methods for the identification of various pesticides that are usually used simultaneously in citrus fruits. The extensive use of diverse classes of pesticides in citrus fruits and their high toxicity may cause serious diseases in the human body. In the current study, a non-enzymatic sensor array has been developed for the identification and discrimination of five different pesticides belonging to diverse classes, including organophosphate, carbamate, and bipyridylium. For this aim, two gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) with different capping agents, citrate and borohydride, were used as sensing elements. The aggregation-induced spectra alterations of AuNPs were utilized to identify the pesticides in a wide range of concentrations (20–5000 ng mL−1). We have employed data visualization methods (i.e., heat maps, bar plots, and color difference maps), a supervised pattern recognition method (i.e., linear discrimination analysis), and partial least squares regression to qualitatively and quantitatively determine the pesticides. Finally, the practical applicability of the developed sensor array was evaluated for the identification of target pesticides in lime peel. The outcomes revealed that the probe could accurately verify the absence or presence of the pesticides in lime fruit.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...