Facile fluorescence strategy for sensitive detection of microcystin-LR based on dsDNA-templated copper nanoclusters†
Abstract
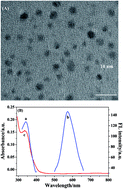
We developed a simple, sensitive, low-cost and label-free method to detect microcystin-leucine-arginine (MC-LR) using double-strand DNA-templated copper nanoclusters (dsDNA-CuNCs) as fluorescent probes. The dsDNA template was designed and fabricated by a MC-LR aptamer strand and its complementary strand, which facilitated CuNCs formation and recognized target MC-LR specifically with strong affinity. The formed fluorescent sensing probe of dsDNA-CuNCs exhibited maximum emission wavelength at 575 nm. Upon addition of target MC-LR into dsDNA-CuNCs, fluorescence was quenched considerably due to the high affinity between MC-LR and the aptamer strand, which indicated a conformational change of the dsDNA-CuNCs probe from the dsDNA structure to single-stranded DNA. Then, the change in fluorescence intensity was used to monitor the MC-LR concentration from 0.01 to 1000 μg L−1 with a limit of detection of 4.8 ng L−1. Compared with previous reports, this method did not require design of a complex DNA sequence, fluorescence dye labels or sophisticated experimental techniques. Moreover, the proposed sensing system could be applicable for detection of target MC-LR in real-water samples.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Bioanalytical sensors for real world applications


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...