A novel bicoumarin-based multifunctional fluorescent probe for naked-eye sensing of amines/ammonia†
Abstract
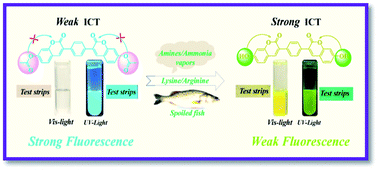
A novel bicoumarin-based fluorescent and colorimetric probe 7,7′-(acetoxy)-3,3′-(p-phenylene)bis(coumarin) (apbis-c) for the highly sensitive detection of amines/ammonia in solution and ammonia vapor in air was constructed for the first time by using the Perkin reaction between 1,4-phenylenediacetic acid and 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde. Instant color changes and real-time fluorescence responses were observed for apbis-c after treatment with different primary and secondary aliphatic amines as well as ammonia in THF/DMSO. Paper-based sensors were prepared by simply depositing apbis-c on filter paper and used in the highly selective and sensitive detection of ammonia vapor in air with an experimental detection limit of 6.85 ppm (the calculated LOD is 0.71 ppm). A plausible mechanism for the fluorescence and colorimetric responses of apbis-c to ammonia was proposed based on 1H NMR study and DFT calculations. In addition, practical studies revealed that apbis-c could be used for the preparation of fluorescent invisible ink, food spoilage indicators and naked eye sensors for lysine/arginine.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...