A new class of ratiometric small molecule intracellular pH sensors for Raman microscopy†
Abstract
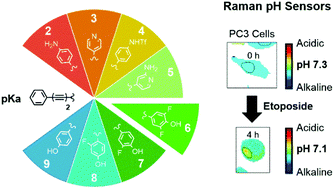
Intracellular pH (pHi) homeostasis is intertwined with a myriad of normal cellular behaviors as well as pathological processes. As such, small molecule probes for the measurement of pHi are invaluable tools for chemical biology, facilitating the study of the role of pH in cellular function and disease. The field of small molecule pHi sensors has traditionally been dominated with probes based on fluorescent scaffolds. In this study, a series of low molecular weight (<260) oligoyne compounds have been developed which exhibit pH sensitive alkyne stretching frequencies (νalkyne) in Raman spectroscopy. The modular design of the compounds enabled tuneability of their pKa(H) through simple structural modification, such that continuous pH sensitivity is achieved over the range 2–10. Alkyne stretching bands reside in the ‘cell-silent’ region of the Raman spectrum (1800–2600 cm−1) and are readily detectable in a cellular environment with subcellular spatial resolution. This enabled the application of a pH sensitive oligoyne compound to the ratiometric sensing of pHi in prostate cancer (PC3) cells in response to drug treatment. We propose that probes based on Alkyne Tag Raman Imaging offer an entirely new platform for the sensing of pHi, complementary to fluorescence microscopy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...