Ensuring high selectivity for preconcentration and detection of ultra-trace cadmium using a phage-functionalized metal–organic framework†
Abstract
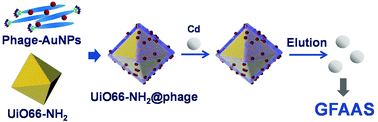
Metal–organic frameworks functionalized with Cd(II) binding phages were for the first time fabricated for the isolation and preconcentration of ultra-trace cadmium. Highly specific Cd(II) binding phages were screened through biological panning from a phage display peptide library. Thereafter, chloroauric acid (HAuCl4) was reduced by the phages to provide phage-stabilized gold nanoparticles (AuNPs). The phage-AuNP networks were then assembled onto the metal–organic framework UiO66-NH2 to serve as an affinity probe for the selective recognition and isolation of ultra-trace cadmium. 2.0 μg L−1 Cd2+ was selectively captured by the derived UiO66-NH2@phage composite with an adsorption efficiency of 100%. UiO66-NH2@phage exhibits favorable anti-interference capability against the coexisting species. It ensures highly selective and sensitive quantification of ultra-trace cadmium with detection by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry (GFAAS). An enrichment factor of 17.4 was obtained along with a limit of detection (LOD) of 3.9 ng L−1 within a linear range of 0.01–0.35 μg L−1. The procedure was further validated by analyzing cadmium content in a certified reference material (CRM, simulated water, GBW08608) and a series of environmental water samples. In general, the present study provides a new protocol for the development of novel adsorbents toward the target by biopanning to regulate the selectivity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...